How 3D Segmentation Transforms AI Model Training for Heart Disease
ILately, using newer 3D segmentation techniques and AI together have been effective in detecting and diagnosing heart issues like an aneurysm and dissection. In this essay, we will see how 3D segmentation is essential to train the AI model accurately and efficiently to detect and diagnose these crucial coronary and cardiovascular conditions.
Why is 3D segmentation important in training AI models?
Segmentation is important when training AI models for heart disease detection and diagnostics. 3D segmentation enables a clear definition of the shape of cardiac structures and abnormalities, unlike 2D imaging. AI algorithms can offer a clearer picture of how complex cardiac conditions manifest by using three-dimensional data.
Aneurysm and dissection are dangerous conditions that must be detected early to allow for effective treatment of the disease. With 3D segmentation, it’s easier to identify things like aneurysms and dissections in the heart’s complicated structures. AI models can study normal and pathological structures like MRIs with high sensitivity and specificity through accurate segmentation of these structures from volume imaging. The 3D segmentation allows detailed anatomical feature extraction from the cardiac imaging dataset and thus enhances the AI model's diagnostic capabilities. It makes it possible to quantify the dimensions, volumes, and morphological characteristics important for measuring the severity and evolution of heart disease aneurysm or dissection.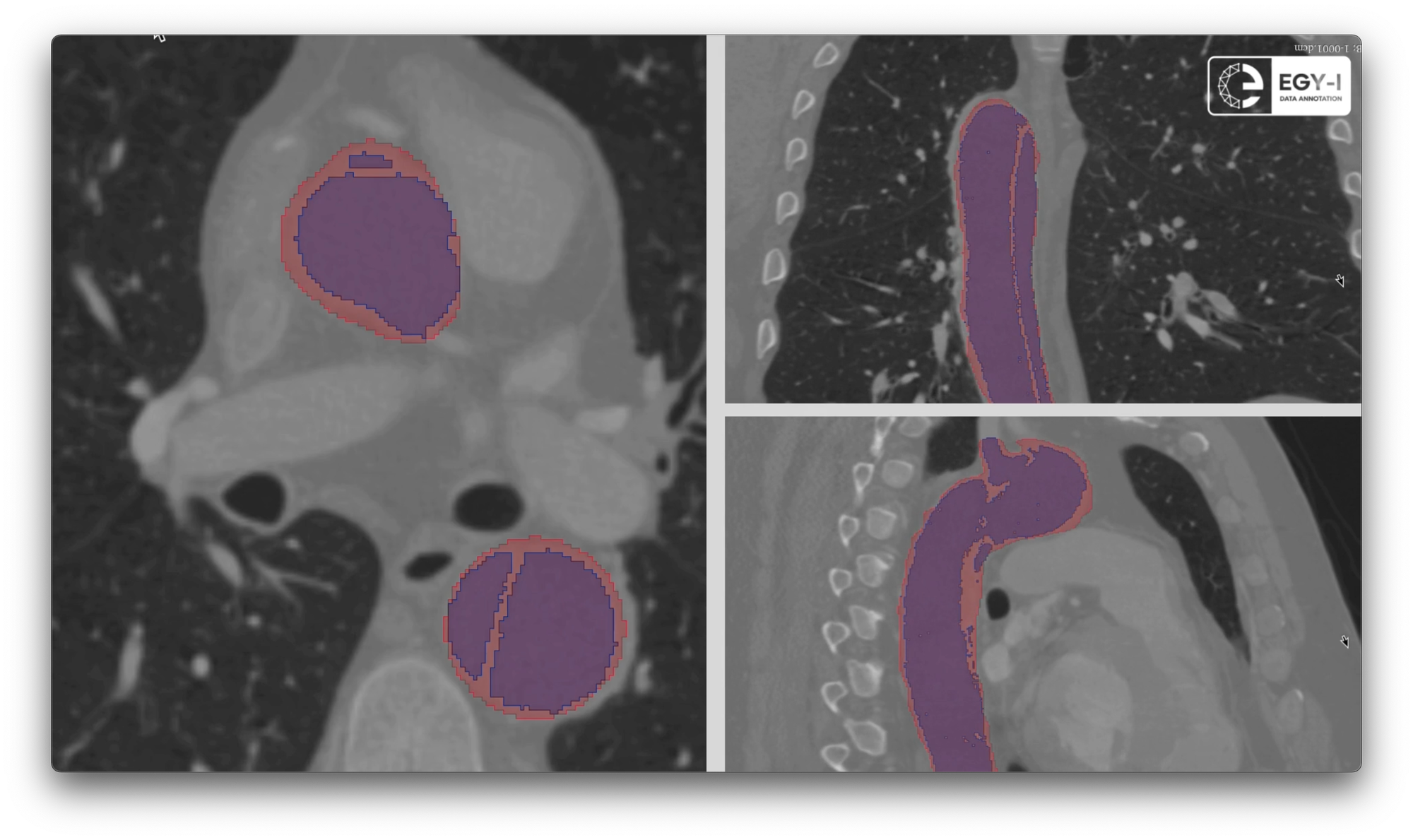
Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities:
Furthermore, 3D segmentation enhances the diagnostic capabilities of AI models by enabling the extraction of detailed anatomical features from cardiac imaging datasets. This allows for the quantification of parameters such as dimensions, volumes, and morphological characteristics, which are essential for assessing the severity and progression of heart diseases like aneurysm and dissection.
Improved Training Data Quality:
By incorporating 3D segmentation into AI model training, the quality of training data is significantly improved. Segmentation ensures that relevant regions of interest within the heart are accurately delineated, reducing ambiguity and enhancing the consistency of annotated data. This results in more robust training datasets, ultimately leading to AI models with enhanced accuracy in detecting and diagnosing cardiac abnormalities.
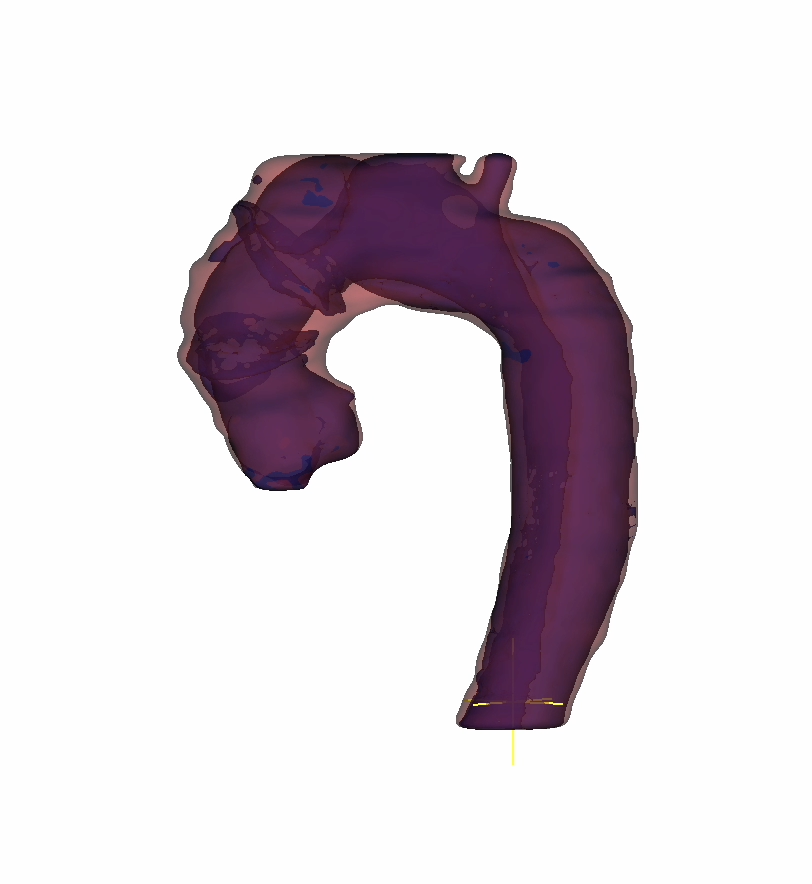
Clinical Implications:
The integration of 3D segmentation with AI model training has profound clinical implications for heart disease management. Accurate detection and diagnosis of aneurysm and dissection through advanced imaging technologies can aid clinicians in making informed treatment decisions, potentially leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced morbidity associated with these conditions.
Conclusion:
3D segmentation is important for training an AI model heart disease detection and diagnosis, especially for aneurysm and dissection. It is important as it helps in a better definition of the cardiac structures and abnormalities in three-dimensions which allows the AI algorithms to analyse the volumetric data thoroughly. This combination will not only allow accurate detection and characterization of life-threatening conditions but will also enhance the diagnostic capabilities of the AI models.
Also, it will extract detailed anatomical features from cardiac imaging datasets. In addition, the quality of training data improves with the inclusion of 3D segmentation in AI model training. Thus, more robust datasets ultimately lead to AI models with improved accuracy regarding cardiac abnormalities. The clinical implications are significant as accurate detection and diagnosis will help clinicians decide on treatment options and improve patient outcomes, as well as reduce morbidity associated with these important cardiovascular events. This means we can combine 3D and AI for a better understanding of a model. The 3D is ShapeNet Model. AI is called segmentation. Together, they will help scientists to better manage heart disease.


